description
Cemented carbides today find a wide range of applications and are tailor-made according to their tasks. Carbide can only be produced by powder metallurgy. The mechanical properties are determined by the composition and granularity of the carbide material, metal binder and any additives. In addition to hardness testing, density testing, structural analysis and porosity tests, non-destructive measurements of magnetization and coercive force are routinely used for quality control according to DIN-ISO 3326. These magnetic properties provide information on the structure, composition and contamination in the sintered state. Although the evaluation draws on a great deal of experience, the measurement results in binary or ternary systems with complex manufacturing processes are often not clearly interpretable.
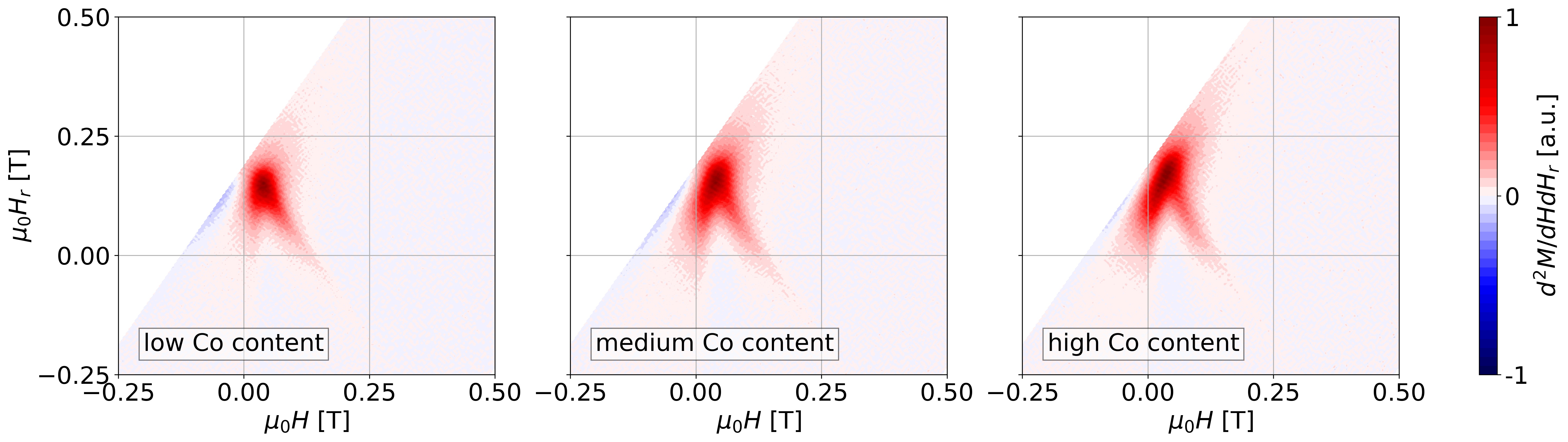
This project aims to make the magnetic characterization of cemented carbides and their conclusions on structural and mechanical properties more accurate. In addition to traditional measurements of M(H)-hysteresis, modern methods such as First-Order-Reversal-Curve (FORC) analysis and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for FORC diagrams will be added, which will make the interpretation more quantitative and clearer.
Today's magnetometers allow FORC measurements to be done within a reasonable time frame of a few minutes. These provide additional information about phase formation and impurities in the powder and sintered state. Despite vast experience, FORC diagrams are not easy to interpret. A so far unused approach should help. We want to interpret the FORC diagrams using Artificial Intelligence. After a learning phase, we expect quantitative statements on structure, composition, phase formation and contamination, as well as on mechanical properties such as hardness, tensile strength, etc. The above improvements are supported by (micro)magnetic simulations. On the one hand, these can calculate FORC diagrams of model systems and make them available to the deep-learning algorithm (or similar: Random Forest for example), and on the other hand, experimental data (M(H) and FORC) can be physically interpreted.
Details
| Duration | 01/04/2020 - 31/03/2023 |
|---|---|
| Funding | FFG |
| Program | |
| Department | |
| Principle investigator for the project (University for Continuing Education Krems) | Univ.-Prof. Dr. Hubert Brückl |
| Project members |
Team
Publications
Brueckl, H.; Breth, L.; Fischbacher, J.; Schrefl, T.; Kuehrer, S.; Pachlhofer, J.; Schwarz, M.; Weirather, T.; Czettl, C. (2024). Machine learning based prediction of mechanical properties of WC-Co cemented carbides from magnetic data only. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, Vol. 121: 106665
Breth, L.; Fischbacher, J.; Kovacs, A.; Özelt, H.; Schrefl, T.; Brückl, H.; Czettl, C.; Kührer, S.; Pachlhofer, J., Schwarz, M. (2023). FORC diagram features of Co particles due to reversal by domain nucleation. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 571 (2023) 170567 Available online 24 February 2023 0304-8853/© 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Vol. 571: 1-6
Lectures
Machine learning based prediction of mechanical properties of Co-WC cemented carbides from magnetic data only
ICM 2024, 05/07/2024
Interpretation ambiguity in FORC diagrams
Joint European Magnetism Symposia Conference JEMS 2022, 28/07/2022
FORC diagrams of hcp-Co particle ensembles from micromagnetic simulations
IEEE Advances in Magnetism (AIM) 2020+2021, 15/06/2021
FORC investigations of large-scale nano-ellipses arrays
AIM 2021, 15/06/2021
Using a Random Forest Regressor to predict First Order Reversal Curves of hcp-Co particle ensembles
Intermag 2021, 26/04/2021

